Hydrotreating is a key process in petroleum product refining, aiming to remove impurities and improve fuel quality. The catalysts used in hydrotreating play a key role in facilitating this process. One of the main goals of hydrotreating is to remove sulfur, nitrogen and other impurities from various crude oil fractions, such as naphtha, vacuum gas oil (VGO) and diesel. This article will provide an in-depth look at the importance of hydrotreating catalysts, specifically in the hydrodesulfurization (HDS) of naphtha and VGO and the hydrodenitrification (HDN) of diesel fuel.
Hydrotreating catalysts are critical to the hydrofinishing process because of their ability to convert unwanted sulfur and nitrogen compounds into their respective hydrogen sulfide and ammonia forms. This conversion is achieved through a series of catalytic reactions that occur under high temperature and high pressure conditions. Two well-known catalysts used in hydrotreating are GC-HP406 and GC-HP448, which are specifically designed for different crude oil fractions.
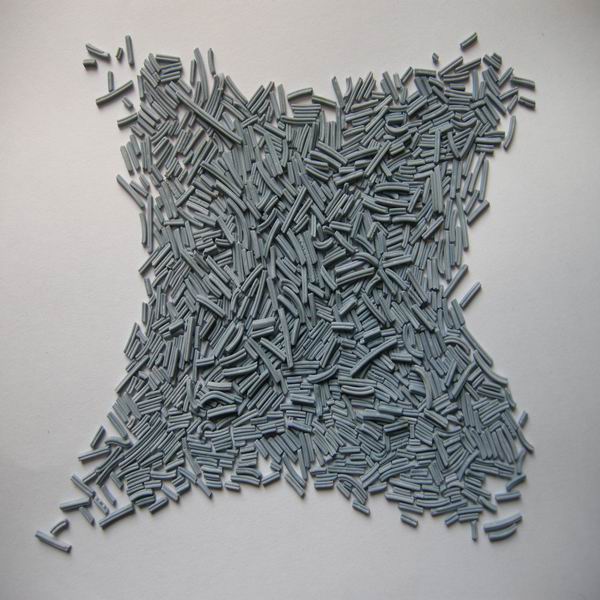
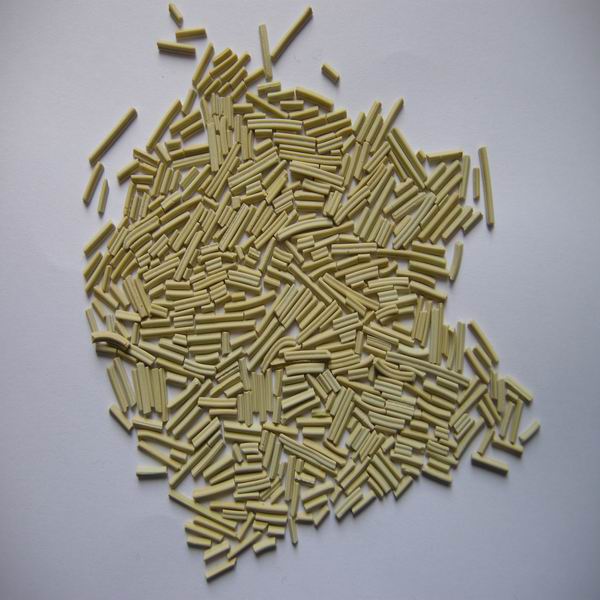


In the case of naphtha, hydrodesulfurization is a key step in hydrotreating since naphtha is the main feedstock for the production of gasoline. The GC-HP406 catalyst is specifically designed to effectively promote the removal of sulfur compounds from naphtha, ensuring that the final product complies with strict environmental regulations and quality specifications. The catalyst plays a vital role in improving the overall quality of gasoline by promoting the conversion of sulfur-containing compounds into hydrogen sulfide.
Similarly, in the hydrotreating of VGO and diesel, both HDS and HDN are essential processes. GC-HP448 catalyst is specially formulated to meet the hydrotreating requirements of VGO and diesel fractions. It effectively removes sulfur and nitrogen compounds, thereby improving the cetane number and overall quality of diesel fuel. Additionally, the catalyst helps reduce sulfur content in VGO, which is critical to meeting sulfur specifications for various VGO-derived end products, such as jet fuel and diesel.
Catalysts used in hydrotreating are engineered to exhibit high activity, selectivity and stability under the harsh operating conditions of the refinery process. They are designed to withstand contaminants and poisons that may be present in the feedstock, ensuring extended catalyst life and consistent performance. Additionally, advances in catalyst technology have led to the development of catalysts with increased resistance to deactivation, helping to increase operating efficiency and cost-effectiveness.
In summary, hydrotreating catalysts are indispensable for the efficient and sustainable production of high-quality petroleum products. The advancement of catalyst technology represented by GC-HP406 and GC-HP448 has greatly promoted the optimization of hydrotreating processes, especially in HDS of naphtha and VGO and HDN of diesel. As the demand for cleaner fuels continues to grow, the role of hydrotreating catalysts in producing high-performance fuels that meet environmental requirements cannot be underestimated. Through continued research and development efforts, there is great promise in the future to further improve the efficacy of hydrotreating catalysts, thereby driving the refining industry towards greater sustainability and efficiency.
Post time: Jul-05-2024

